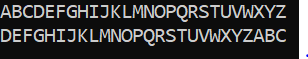
The Caesar cipher is one of the earliest known and simplest ciphers; Created and used in 44 BC by Julius Caesar. It is a type of substitution cipher in which each letter in the plain text is 'shifted' with certain number of places in the alphabet. For example, if we right shift the alphabets by 3 char then we get the below text; So now if we encrypt the message with above "TEST MESSAGE" will show below result The encryption can be represented Mathematical, by first transforming the letters into numbers, like A = 0, B = 1,…, Z = 25. To represent the Caesar Cipher encryption function, e(x), where x is the character we are encrypting, as: E(X) = (X+K) (mod 26) Where K represents key used to shift the letters in alphabets. for decryption we can use below equation E(X) = (X-K) (mod 26) I have written the below code which accept user input and right shift the alphabets by 9 char: Result produce by o...


Comments
Post a Comment